α, β and γ Radiations
α, β and γ Radiations: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Radioactivity, Alpha Decay, Energy Level Diagram for Gamma Decay & Beta Stability Curve etc.
Important Questions on α, β and γ Radiations
Out of the two characteristics – the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z) – of a nucleus, which one does not change during nuclear decay?
Out of the two characteristics – the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z) – of a nucleus, which one does not change during nuclear decay?
Which are amongst the following represent plot of the distribution of kinetic energy of particles?
particle is emitted in a radio active reaction when
When Boron nucleus is bombarded by neutrons, - particles are emitted. The resulting nucleus is of the element _____________ and has the mass number_____________
In the Uranium radioactive series, the initial nucleus is and the final nucleus is . When the Uranium nucleus decays to lead, the number of particles emitted is _______________ and the number of particles emitted is _______________.
In the given nuclear reaction, the element is
A nucleus of mass at rest, is initially in an excited state whose energy is above the ground state of the nucleus. The nucleus emits a gamma-ray of energy and makes a transition to the ground state. Now choose CORRECT statement(s)
converts to by positive decay as well as electron capture. Let values for the decay and electron capture be and respectively in the above reaction.
Just after a shell capture, which of the following come out from the atom?
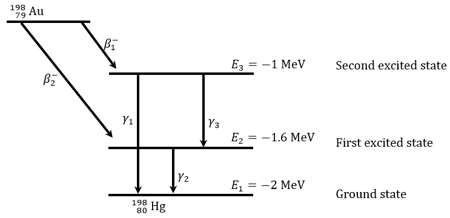
Gold Nucleus can decay into mercury nucleus by two decay schemes shown in figure. (i) It can emit a particle and come to ground state by either emitting one ray or emitting two rays (ii) It can emit one particle and come to ground state by emitting ray. Atomic masses: The energy levels of the nucleus are shown in figure.
In beta decay, the emitted beta particles have a range of values of their kinetic energy. The maximum energy of beta particles emitted in the decay of is . Assuming number of beta particles () with energy between and have the form . Let a sample of is decaying into and activity is kept constant at rate millicurie. All beta particles emitted are being absorbed by a target and causing evolution of heat. If the heat evolution rate is , find
Let nuclide be emitter and nuclide be emitter. Both and contain large number of nuclei. Choose the correct statement:
Out of the two characteristics – the mass number (A) and the atomic number (Z) – of a nucleus, which one does not change during nuclear decay?
In a radioactive decay chain, the initial nucleus is . At the end, there are -particles and -particles which are emitted. If the end nucleus is and are given by:
In a radioactive decay chain, the initial nucleus is . At the end there are particles and particles which are emitted. If the end nucleus is and are given by
A radioactive nucleus converts into a stable nucleus . The half-life of is . Calculate the age of radioactive sample when the ratio of and is .
